Gallstones and kidney stones might sound like they belong in the same category, but they’re quite different. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. In this article, we’ll delve into the unique characteristics of gallstones and kidney stones, answering the questions “Are gallstones and kidney stones the same” and exploring their causes, symptoms, and treatment options to shed light on their differences.
Table of Contents
Gallstones: What You Need to Know
Let’s start by unraveling the mystery of gallstones. These little troublemakers form in the gallbladder, a small organ beneath the liver. Gallstones are typically made of hardened cholesterol or bilirubin, a pigment produced by the liver. They can range in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball, causing significant discomfort when they block the flow of bile.
Symptoms of gallstones include:
- Intense abdominal pain, usually in the upper right portion.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Jaundice, indicated by yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Digestive issues, such as bloating and gas.
Now, let’s switch gears and talk about kidney stones.
Kidney Stones: The Lowdown
Unlike gallstones, kidney stones form in the kidneys, those bean-shaped organs responsible for filtering waste from the blood and producing urine. Kidney stones are crystallised minerals and salts that clump together, creating painful obstructions in the urinary tract.
Here are some telltale signs of kidney stones:
- Severe pain in the side and back, often radiating to the lower abdomen and groyne.
- Blood in the urine, giving it a pink, red, or brown hue.
- Frequent urination, accompanied by a sense of urgency.
- Nausea and vomiting.
Now, onto the burning question: Are gallstones and kidney stones the same?
Gallstones vs. Kidney Stones: Spotting the Differences
While both gallbladder stones and kidney stones share symptoms like abdominal pain and nausea, several key differences set them apart:
- Location: Gallstones form in the gallbladder, whereas kidney stones form in the kidneys. This variance in location accounts for differences in symptoms and treatment approaches.
- Composition: Gallstones are primarily composed of hardened cholesterol or bilirubin, whereas kidney stones are made of crystallised minerals like calcium, oxalate, or uric acid. Understanding the composition is crucial for determining the most effective treatment plan.
- Pain Patterns: The pain associated with gallstones tends to concentrate in the upper right abdomen, whereas kidney stone pain typically radiates from the side and back to the lower abdomen and groyne. This distinction can aid healthcare providers in diagnosing the underlying issue.
What are the Risk factors associated with Gallstones vs Kidney Stones?
Risk Factors for Gallstones:
- Gender: Women are more prone to developing gallstones than men, particularly those who are pregnant, taking hormone replacement therapy, or using birth control pills. This is often attributed to hormonal fluctuations that affect bile production and gallbladder function.
- Age: Gallstones are more common in individuals over 40, with the risk increasing with age. As people age, the gallbladder becomes less efficient at emptying bile, leading to the formation of gallstones.
- Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly obesity, is a significant risk factor for gallstones. Obesity can disrupt the balance of cholesterol and bile salts in the bile, promoting the formation of gallstones.
- Dietary Factors: Diets high in cholesterol and fat and low in fibre can contribute to the development of gallstones. Consuming excessive amounts of refined carbohydrates and processed foods may also increase the risk.
- Rapid Weight Loss: Crash diets or rapid weight loss programs can increase the risk of gallstones. When the body metabolizes fat during rapid weight loss, the liver releases more cholesterol into the bile, which can lead to the formation of gallstones.
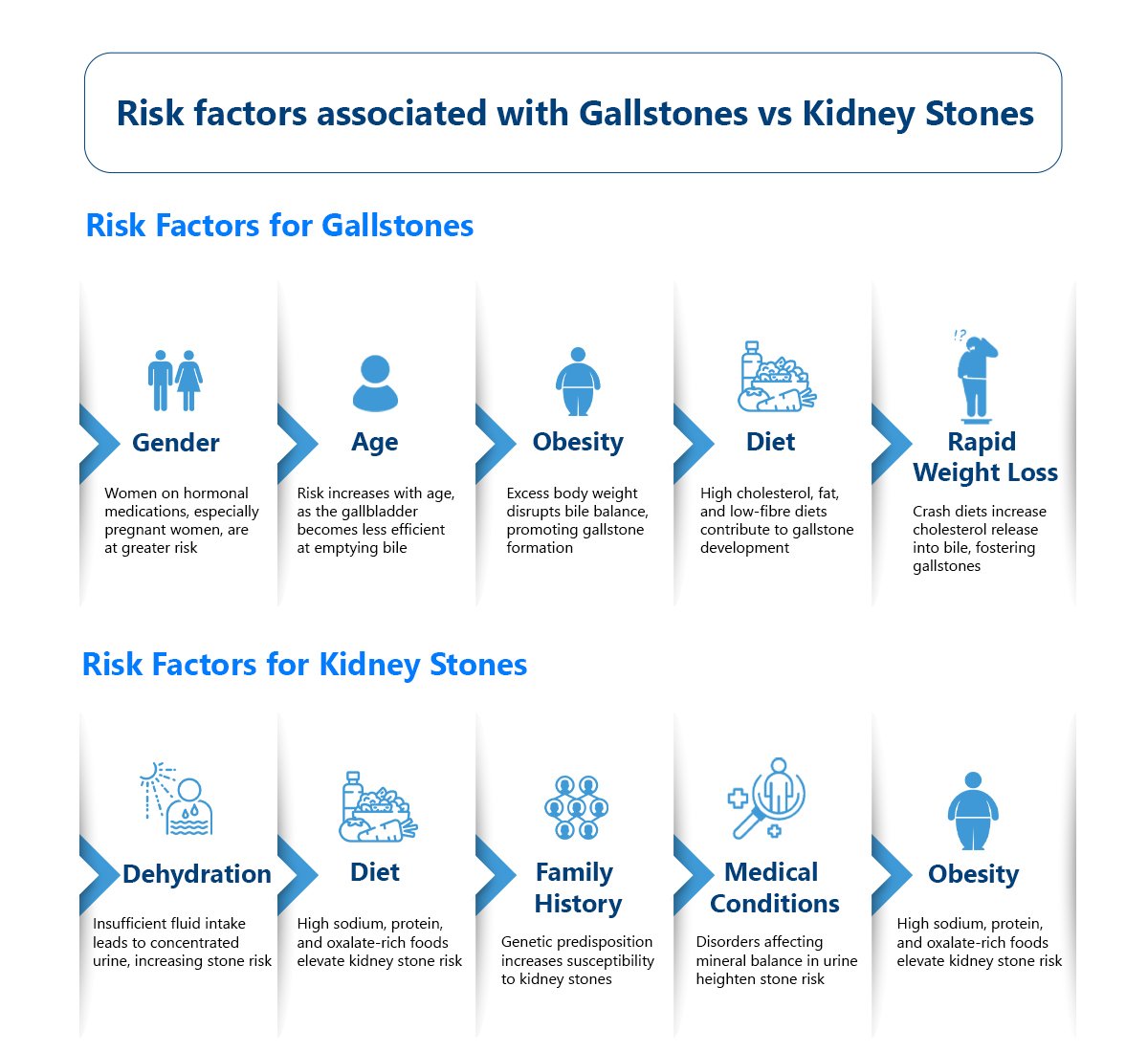
Risk Factors for Kidney Stones:
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can lead to concentrated urine, which increases the risk of kidney stone formation. Dehydration can occur due to inadequate fluid intake, hot weather, excessive sweating, or certain medical conditions.
- Dietary Factors: Consuming a diet high in sodium, protein, and oxalate-rich foods (such as spinach, rhubarb, nuts, and chocolate) can increase the risk of kidney stones. Excessive intake of certain vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D and calcium supplements, may also contribute to stone formation.
- Family History: Like gallstones, a family history of kidney stones can increase an individual’s risk of developing them. Genetic factors may predispose certain individuals to kidney stone formation.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hyperparathyroidism, renal tubular acidosis, and cystinuria, can increase the risk of kidney stones. These conditions affect the balance of minerals and salts in the urine, making stone formation more likely.
- Obesity: Obesity is a risk factor for kidney stones, as it can lead to changes in urine composition and metabolism that promote stone formation.
Treatment Options: What You Need to Know
When it comes to treating gallstones vs kidney stones, healthcare providers have several options at their disposal:
- Gallstones: In mild cases, dietary changes and medication may help dissolve gallstones. However, if the stones are causing severe symptoms or complications like infection or pancreatitis, surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) may be necessary.
- Kidney Stones: Treatment for kidney stones depends on their size and composition. Small stones may pass through the urinary tract with ample hydration and pain medication. Larger stones may require extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), a procedure that uses sound waves to break up the stones, or surgical removal via ureteroscopy or percutaneous nephrolithotomy.
Conclusion:
In summary, gall bladder stone vs kidney stone may share some similarities in symptoms, but they differ significantly in their location, composition, and treatment approaches. By understanding these distinctions, individuals can seek appropriate medical attention and embark on the path to relief.
Whether it’s a gallstones vs kidney stones issue, prompt diagnosis and intervention are key to alleviating discomfort and restoring optimal health. If you are also seeking such treatment, do contact Dr Dushyant Pawar, he is one of the top urologists in Ahmedabad. He is currently working at Shivanta Multispeciality Hospital as a Laparoscopy surgeon and a prostate cancer specialist. He is renowned for his prolonged practice in kidney cancer treatment, and prostate surgery.
FAQs
Q: What causes gallstones and kidney stones?
A: Gallstones form from hardened bile in the gallbladder, while kidney stones develop from mineral buildup in the kidneys.
Q: What are the symptoms of gallstones and kidney stones?
A: Symptoms of gallstones include abdominal pain, nausea, and jaundice, whereas kidney stones may cause severe back or abdominal pain, nausea, and blood in urine.
Q: How are gallstones and kidney stones diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests like ultrasound for gallstones and CT scans for kidney stones, along with analysis of symptoms and medical history.
Q: Can gallstones or kidney stones be prevented?
A: Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding certain risk factors can help prevent both gallstones and kidney stones.
Q: Are gallstones and kidney stones dangerous?
A: While both conditions can cause severe pain and complications, prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.