As you get older and after having children, women are more prone to experience an overactive bladder (also known as urine frequency). Overactive bladder symptoms can occur in men who have an enlarged prostate. Urinary frequency can also be a side effect of diabetes, certain drugs, and neurological conditions.
Table of Contents
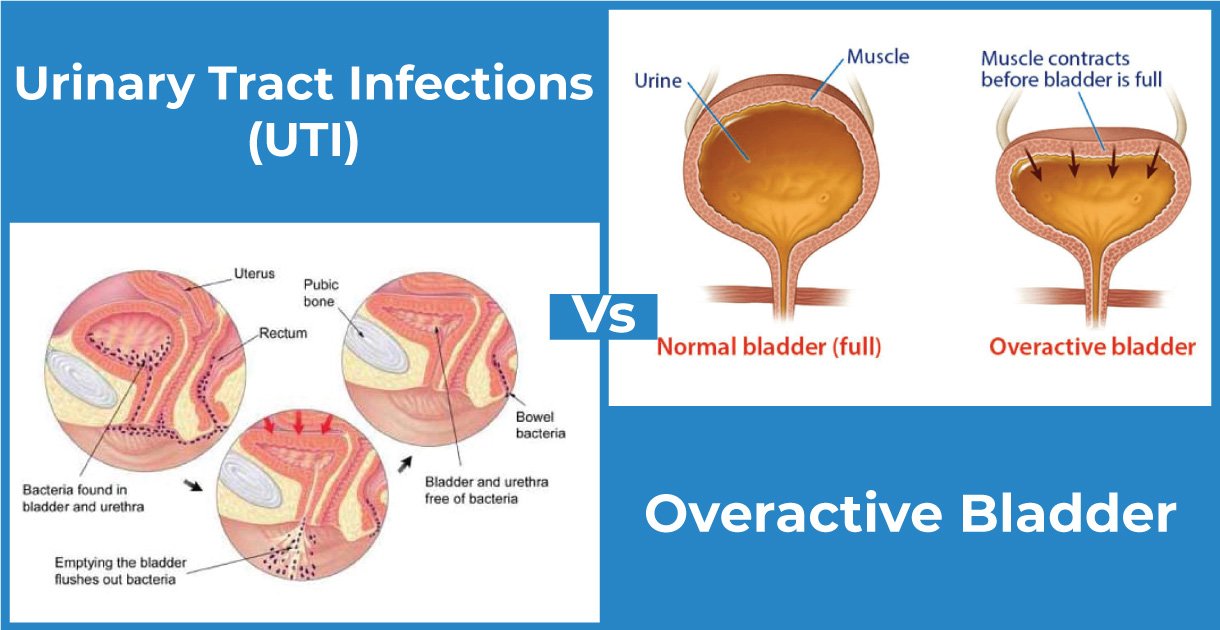
Bladder Anatomy
- When full, your bladder holds between one and a half and two cups (400 and 600 milliliters) of urine.
- The muscles of your pelvic floor are located underneath your bladder.
- The urethral sphincter, a band of muscles that surrounds the urethra, aids in keeping the tube that delivers pee closed and supports your pelvic organs.
- The purpose of these muscles is to keep the bladder tightly closed to prevent urine leaks. They are essential for bladder control.
- People with an overactive bladder often lose bladder control and involuntary loss of urine.
- The most typical form of incontinence is stress incontinence. It only takes a giggle, a cough, or movement to start leaking. Despite how much urine is in the bladder, people with urge incontinence experience frequent and unexpected urination needs.
An overactive bladder may negatively impact your daily activities and general way of life. These ten techniques will help you control your overactive bladder.
10 Ways to Control Your Overactive Bladder
-
Try to avoid caffeine, carbonated drinks, sugar, alcohol, and spicy or acidic foods
- Because caffeine is a diuretic, you will need to use the restroom more frequently.
- Sugar and carbonated beverages are thought to stimulate the bladder.
- Drinking alcohol prevents your body from concentrating urine. As a result, you tend to urinate more weak, watery urine, which causes you to get dehydrated.
- Hot or acidic food may trigger your overactive bladder and worsen your symptoms since you are dehydrated. Your bladder can also become irritated by some sour fruits and drinks, such as orange, grapefruit, lemon, and lime.
-
Losing weight may help to improve your bladder control
Too much weight strains the pelvic floor muscles, resulting in an overactive bladder and a loss of bladder control. You’ll have better bladder control if you can shed even a little weight.
The most exemplary weight loss programs always incorporate a nutritious diet, regular exercise, and setting attainable goals. Fad diets are frequently successful in the short term, but they rarely result in long-term weight loss because once you get bored with the diet, you often revert to bad eating patterns that are engrained in your life.
-
Pelvic floor exercises can help immensely
Although your pelvic floor muscles are not visible, they nonetheless lose strength if they are not used, much like other muscles in your body. Exercises for the pelvic floor, often known as “Kegel exercises,” assist the pelvic floor in becoming stronger when performed faithfully at least twice each day.
-
Carefully manage your fluid intake
When you consume too much fluid, your bladder becomes overworked, and you need to urinate. When you drink too little, your urine concentrates, irritating your bladder and causing urinary urgency. To prevent dehydration, it’s crucial to keep up your fluid intake. To keep well-hydrated during the day, you can sip water slowly.
-
Smoking may increase the urge to urinate
Smoking makes you cough and irritates the bladder lining, both of which are harmful if you have an overactive bladder.
Stopping smoking is a wise choice for general health and overactive bladder reasons. Start a formal “Quit Smoking” program with the help of your doctor for the best results, which may include smoking cessation drugs and support groups.
-
Discuss FDA-approved therapies with your doctor
Numerous drugs are available to treat an overactive bladder, exercise, and behavioral changes. One medication, Oxysterol for Women, is even sold as an OTC patch that needs to be changed every four days. The negative effect of dry mouth may be less common with extended-release versions.
-
Keeping a “bladder diary” may help identify triggers
Although it may seem time-consuming, keeping a journal will allow you and your doctor to pinpoint any triggers for your overactive bladder and track how frequently you use the restroom each day.
How should someone with an overactive bladder keep a journal?
- Specify the types and amounts of fluids you consume.
- Record the kind and amount of food you consume.
- Keep track of your bathroom visits and indicate whether they were effective (there was no pee leaking).
- Describe what you were doing when the need to urinate or a leakage happened (for example: running, sneezing, exercise, general movement, or just sitting)
-
Absorbency products can help
No matter how quickly you can run, there are occasions when the distance to the bathroom is simply too far. Don’t put yourself in an awkward predicament. There is a large selection of discrete and cozy products accessible. Many incontinence products are on the market, including disposable adult-sized underwear with built-in absorbency and easy-tear sides and discreet pads with low bulk that can be put into underwear. Men and women have distinct needs, and various reusable and washable goods are available to accommodate this.
-
Seek help from a qualified physical therapist
The ligaments, nerves, and pelvic floor muscles that support the vagina, bladder, and urethra can become damaged during vaginal deliveries. While some women may benefit from pelvic floor exercises after giving delivery, many require more rigorous physical treatment.
If you experience any incontinence or pain that persists after giving birth, talk to your doctor, who may recommend getting treatment from a licensed physical therapist specializing in pelvic floor therapy. Starting a thorough rehabilitation program immediately after giving birth may prevent you from experiencing later, more gynecological severe issues.
-
Take charge: Seek your doctor’s advice
Only one in twelve persons with incontinence concerns seek help, despite 80% of those suffering from urine incontinence can be cured or improved. Discuss bladder control with your doctor because it can significantly enhance your quality of life.
Your doctor can perform an investigation to identify the root of your overactive bladder. Then, the appropriate course of action can be determined, including drugs, bladder training, pelvic floor exercises, absorbent items, surgery, or a combination of these.
Conclusion
A combination of symptoms known as an overactive bladder can include frequent urination urges and nighttime urination. Weak muscles, nerve injury, pharmaceutical use, alcohol or caffeine use, illness, and being overweight are some of the potential causes. Adapting your way of life could be beneficial. Treatment for overactive bladder might be challenging to administer. However, a lot of people are pleased with the care they get and frequently see a significant increase in their quality of life. Your doctor will advise you on the best initial actions to take and present you with your options for any future treatments you might require. If you are curious about the treatments available to control overactive bladder, schedule an appointment with Urologist Surgeon Dr. Dushyant Pawar for the best overactive bladder Treatment!